Derek Leary | Oct. 23, 2013 1:56AM EDT

By Derek Leahy
The international pipeline safety expert who last August described Enbridge’s Line 9 pipeline as “high risk for a rupture” now says the probability of Line 9 rupturing is “over 90 percent.”
“I do not make the statement ‘high risk for a rupture’ lightly or often,” said Richard Kuprewicz in an interview with DeSmog Canada. “There are serious problems with Line 9 that need to be addressed.” Kuprewicz is a pipeline safety expert with over forty years of experience in the energy sector.
Hundreds rallied in Toronto over the weekend to voice their opposition to Enbridge’s plans to ship Alberta tar sands bitumen from Sarnia to Montreal through the 37-year-old Line 9 pipeline.
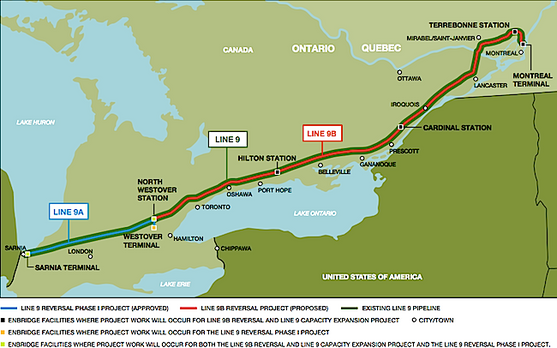
Kuprewicz also expressed concerns about transporting diluted bitumen through Line 9 saying it will increase the growth rates of cracks on the pipeline. Line 9 lies in the most populated part of Canada and crosses the St. Lawrence River and major waterways flowing into Lake Erie and Lake Ontario. A Line 9 spill could pollute the drinking water of millions of Canadians.
No Line 9 rally in Toronto, Canada, Oct. 19. Photo credit: Katheleen Quinn
Extensive Stress Corrosion Cracking on Line 9
“Existing SCC (stress corrosion cracking) on Line 9 can worsen due to the increase in pressure cycling associated with shipping dilbit (diluted bitumen),” explained Kuprewicz. “This could lead to a rupture.”
The thick heavy crude bitumen is diluted with a condensate (natural gas or naphtha) so it can flow through pipelines. ‘Pressure cycling,’ or the variations in operating pressures of a pipeline, increase with dilbit, because dilbit can vary more in composition than light conventional oil. The greater swings in the levels of operating pressures can create cracks in a pipeline.
Kuprewicz examined Enbridge’s assessments of Line 9 and found evidence of extensive stress corrosion cracking on Line 9, most likely caused by the pipeline’s external protective coating (polyethylene tape or PE-tape) separating from the sections of Line 9, allowing water to damage the pipeline.
Kuprewicz has seen this problem before. He researched the U.S. federal investigation into the Kalamazoo, MI, dilbit spill—the largest onshore oil spill in US.. history—on behalf of various concerned parties. The disbondment of PE-tape on Enbridge’s Line 6B pipeline and subsequent SCC on the pipe caused the rupture. Three million litres of dilbit were spilled into the Kalamazoo River and the surrounding waterways, and the $1 billion cleanup continues to this day.
Enbridge claims that its in-line inspection tool can detect any serious SCC threats to the pipeline. According to Kuprewicz, the in-line detection technology Enbridge is using has yet to be proven effective.

Hydrostatic Testing of Pipelines is the “Gold Standard” for Safety
“Enbridge needs to conduct a hydrostatic test on Line 9,” Kuprewicz told DeSmog Canada. “It is the gold standard for pipeline integrity and safety. Canada has a well-established history of hydrotesting its pipelines.”
A hydrostatic test would pump water through Line 9 at similar pressures to those the pipeline is expected to operate at, but there is no indication that Enbridge plans to conduct hydrostatic testing.
Kuprewicz also questions Enbridge’s claims of an automatic shutdown in the event of a pressure drop in Line 9 or a 10-minute shutdown if an unexplained reading comes in from the pipeline. When a pipeline ruptures, pressure loss as well as detecting the drop can take quite a while. The 10-minute shutdown procedure existed at the time of the Kalamazoo spill and it still took Enbridge 17 hours to shut down the ruptured pipeline.
“I am not trying to be hard on Enbridge. There are definite improvements they could make to their pipeline management system that would significantly reduce the chances of a Line 9 rupture,” said Kuprewicz.
Enbridge Lacks Adequate Liability Insurance for a Line 9 Spill
The Goodman Group Ltd found that, in the event of a Line 9 spill, Enbridge’s $685 million liability insurance for all its operations (not just Line 9) would be inadequate. The California-based consulting firm says Enbridge needs $3 billion of liability insurance for Line 9 alone.
“This is especially true in Toronto and Montreal, where the pipeline runs parallel to or across key urban infrastructure and could threaten the drinking water supply, resulting in multi-billion dollar costs,” warned Ian Goodman, president of the Goodman Group.
Cleanup costs of other onshore oil spills such as Lac-Megantic in Quebec and the Kalamazoo spill were analyzed by the Goodman Group, and Line 9’s location in a highly populated area was considered. The firm concluded that a bad Line 9 spill would cost at least $1 billion. The worst-case scenario was pegged between $5-10 billion.

Ontario Demands Independent Third-Party Assessment of Line 9
The Ontario government in some ways echoed the recommendations of Kuprewicz and the Goodman Group on Oct. 17 during a National Energy Board (NEB) public hearing in Toronto.
Ontario demanded that Enbridge conduct a hydrostatic test on Line 9, and that the company maintain $1 billion in insurance for the pipeline. The province also called on the NEB to initiate an independent third party assessment on the state of Line 9, and not rely solely on Enbridge’s findings.
“Given the age of the pipeline, its location in a large part of southern Ontario, its additional service life of 30 years or more, and the potential adverse consequences of a rupture, it seems a matter of simple prudence and common sense to ensure the (assessments) are as thorough, comprehensive and as accurate as possible,” Rick Jennings told the NEB panel. Jennings is an assistant deputy minister with Ontario’s Ministry of Energy.
“In our view, an independent third-party review is required for that assurance,” said Jennings.
The NEB hearings on Line 9 were scheduled to wrap up in Toronto on Oct. 19, but the NEB postponed the final hearing to an unknown date and location. The NEB could make its final decision on Line 9 as early as January 2014.
Enbridge has applied with the NEB to increase the capacity of Line 9 from 240,000 to 300,000 barrels per day, reverse the pipeline to flow west-to-east and ship ‘heavy crudes’ such as dilbit through the line.
Critics of the Line 9 project say the pipeline should not be approved to ship dilbit because of the likelihood of a rupture and the adverse impacts that further expansion of the tar sands will have on climate change and the people and environment of northern Alberta.
SOURCE ARTICLE: https://www.ecowatch.com/hundreds-protest-tar-sands-pipeline-as-expert-warns-of-90-percent-prob-1881802483.html
